Introduction
If you work in IT audit, compliance, cyber security, or internal controls, you already know one thing: weak IT General Controls (ITGCs) can instantly break your audit results and create unnecessary risks for the business.
That’s why having a clear, practical, and actionable ITGC checklist is essential.
In this blog, you’ll get:
- A ready-to-use ITGC Audit Checklist
- The best practices for ITGC implementation
- A step-by-step approach to pass internal, external, or SOX audits smoothly
- Templates, examples, interview questions, and more
Let’s get started.
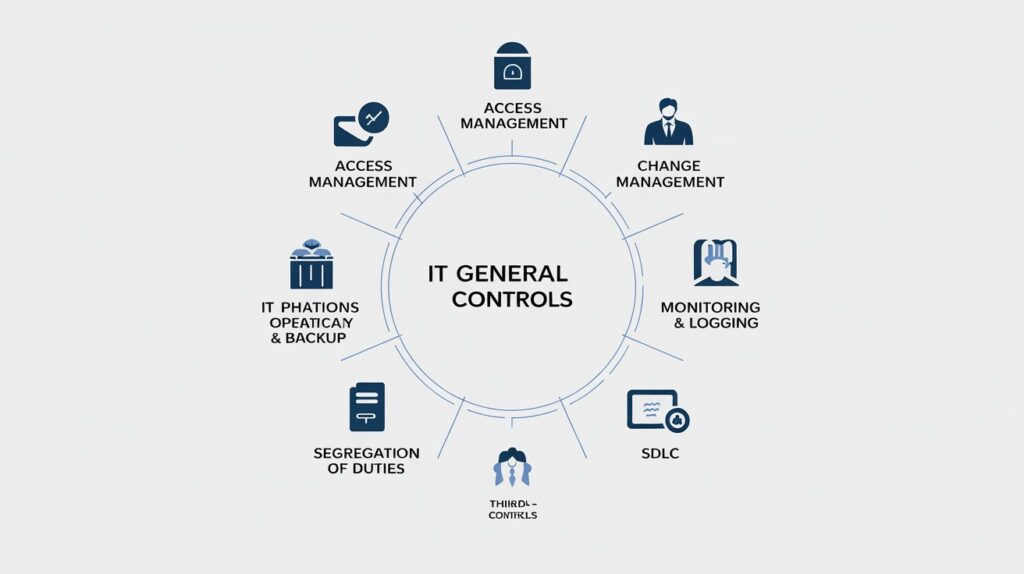
What Are IT General Controls (ITGCs)?
IT General Controls are foundational IT policies and procedures that ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems.
They support reliable financial reporting, protect business applications, and prevent unauthorized access or changes.
ITGCs typically cover:
- Access controls
- Change management
- IT operations
- Backup & recovery
- Security monitoring
- Vendor controls
- Physical & environmental controls
Why Are ITGCs Important?
Strong ITGCs help organizations:
- Achieve SOX compliance
- Reduce internal and external audit findings
- Prevent data breaches and fraud
- Maintain reliable system operations
- Provide accurate financial reporting
Without solid ITGCs, even the best applications or financial systems become risky.
Core ITGC Categories
1. Access Management
Controls for adding, modifying, and removing user access.
2. Change Management
Controls for managing changes to systems and applications.
3. IT Operations
Includes job scheduling, backups, patching, and system monitoring.
4. Segregation of Duties (SoD)
Ensures no single user has excessive privileges that can create risk.
5. SDLC (System Development Life Cycle)
Covers development, testing, and deployment of software.
6. Physical & Environmental Security
Protects physical infrastructure and data centers.
7. Vendor & Third-Party Controls
Monitors risks related to outsourced systems or services.
8. Monitoring & Logging
Ensures logs exist and are reviewed regularly.
ITGC Audit Checklist (2025 Edition)
A. Access Management Controls
- Documented user provisioning and deprovisioning process
- No shared accounts (or documented exceptions)
- Strong password policy (or MFA for critical systems)
- Quarterly access reviews with evidence
- Privileged Access Management (PAM) in place
- Access logs retained and monitored

B. Change Management Controls
- Formal change request with justification
- Risk assessment and testing evidence
- CAB (Change Advisory Board) approval
- Segregation between developers and production deployers
- Emergency change process with retro approval
- Deployment logs and rollback plans

C. IT Operations & Patch Management
- Patch management schedule and automated updates
- Daily operational checks and monitoring
- Backup schedule with periodic restore testing
- Antivirus updates across all endpoints
- Job scheduling and monitoring alerts
D. Segregation of Duties (SoD)
- SoD matrix for critical applications
- Periodic review of conflicts
- Compensating controls documented
- Approval workflow for exceptions
E. SDLC Controls
- Defined SDLC policy
- Requirement documentation
- Code review and peer validation
- UAT sign-off evidence
- Version control in place
- Production deployment approval
F. Physical & Environmental Controls
- Restricted access to server rooms/data centers
- CCTV monitoring with retention
- UPS/Generator maintenance logs
- Fire and environmental sensors
G. Vendor & Third-Party Controls
- Vendor risk assessment
- SOC 1/SOC 2 reports (if applicable)
- SLA compliance review
- Access control for vendor accounts
H. Monitoring & Logging Controls
- Centralized logging (SIEM)
- Retention policy for logs
- Daily/weekly log review
- Incident response plan
- Evidence of incident handling
Best Practices for ITGC Implementation
- Prioritize high-risk applications first
- Automate access reviews, logs, and evidence collection
- Maintain clear documentation for auditors
- Train teams on change procedures and SoD
- Run internal pre-audits every quarter
- Build dashboards for monitoring critical controls
- Keep evidence centralized and timestamped
- Review controls annually and update policies
Step-by-Step ITGC Implementation Roadmap
0–30 Days: Assessment
- Identify all systems and owners
- Map controls to each system
- Prioritize based on risk
31–60 Days: Quick Wins
- Enforce MFA
- Start access reviews
- Enable log retention
- Patch critical systems
61–90 Days: Automation
- Integrate IAM and PAM tools
- Automate deployments and patching
- Perform first restore test
Quarterly
- Review all controls
- Fix gaps
- Update documentation
ITGC Interview Questions (Quick Prep)
Q1. Why are ITGCs important for SOX compliance?
They ensure accurate financial reporting by safeguarding systems involved in financial processes.
Q2. What is the difference between access and authorization?
Access = ability to log in
Authorization = permissions after logging in
Q3. How do you perform an access review?
Export users → Review with owner → Remove excess access → Document approvals.
Q4. What evidence is needed for change management?
Tickets, approvals, test results, deployment logs, rollback plan.
Conclusion
Implementing strong ITGCs is not just about passing an audit — it helps build a secure, reliable, and well-controlled IT environment. Use this checklist regularly and keep improving your control maturity.
If you need templates or help preparing for ITGC/SOX roles, MTJ Job Solutions provides hands-on training and real-time project guidance.
